云服务器性能高的费用太高,特别是学习ai(人工智能后)。内网的实体服务器性价比高,但是访问和使用不方便。
现在开始使用frp内网穿透服务,将内网服务器映射到公网。特此记录。
https://github.com/fatedier/frp
安装和配置都很简单。启动服务器和客户段即可。
服务器防火规则
#### frp nat
# bind
-A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp –dport 7000 -j ACCEPT
# ssh
-A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp –dport 7022 -j ACCEPT
# mysql
-A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp –dport 33306 -j ACCEPT
####
# bind
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp –sport 7000 -j ACCEPT
# ssh
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp –sport 7022 -j ACCEPT
# mysql
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp –sport 33306 -j ACCEPT
Author Archives: 张 子萌
esp8266连接mqtt服务订阅消息、接收推送
raspberry pi上安装mqtt服务器。
apt-get update
apt-get install mosquitto
apt-get install mosquitto mosquitto-clients python-mosquitto
apt-get install python-mosquitto
启动mqtt服务
mosquitto
检查mqtt服务是否启动。默认1883端口。
netstat -antp
结果
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1883 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 383/mosquitto
查看服务器详细信息命令
/etc/init.d/mosquitto status
esp8266源码
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import network
from mqtt import MQTTClient
import machine
import time
# 连接WIFi
sta_if = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF); sta_if.active(True)
#sta_if.scan()
sta_if.connect("SID", "密码")
while not sta_if.isconnected():
machine.idle()
# 根据订阅内容开关灯
def sub_cb(topic, msg):
if int(msg) == 0:
machine.Pin(int(12), machine.Pin.OUT, value=0)
elif int(msg) == 1:
machine.Pin(int(12), machine.Pin.OUT, value=1)
# 连接mqtt服务器
client = MQTTClient(client_id="1", server="192.168.1.212", port=1883)
client.set_callback(sub_cb)
client.connect()
# 循环获取内容
while True:
client.subscribe(topic="simonzhang/net")
time.sleep(0.5)
esp8266的mqtt lib地址如下。将mqtt.py和主文件命名为main.py上传到esp8266。
https://github.com/simon-zzm/ESP8266-lib/blob/master/mqtt.py
重启esp8266,在raspberry pi上推送消息控制灯开关成功。
开灯
mosquitto_pub -t simonzhang/net -m “1”
关灯
mosquitto_pub -t simonzhang/net -m “0”

其它记录
命令行
mosquitto_sub -t simonzhang/net
-t 指定订阅主体(topic),主体不用提前设定,直接发布就行。
mosquitto_pub -t simonzhang/net -m “Hello, simonzhang!”
-m 为发送内容
订阅名称可以用 + 代替,例如:
simon/+/zhang/+
这样就可以推送,“simon/hello/zhang/led”的主体。
#号应用于主体的结尾,例如:
simon/hello/zhang/led#
需要研究的还有通讯加密,程序加密和耗能部分。
ESP8266 python3 直接使用 gy-39 传感器
gy-39放在raspberry移动不太方便,耗电量也大,只为收集数据有点浪费,直接用esp8266。
ESP8266也烧成python环境。省略配置wifi部分。
将附件中lib上传,ESP8266的lib与rasbperry不同。
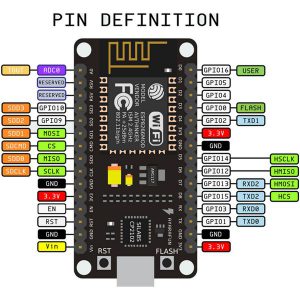
ESP8266接口图。
板子上的D1和D2对应的是ESP8266上的4,5脚,连接如图。
到ESP8266查看硬件连接
>>> from machine import Pin, I2C
>>> i2c = I2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
>>> i2c.scan()
[74, 118]
转换十六进制算一下,两个传感器已经都认到了,文档在raspberry pi连接GY-39文档中。
查看上传文件
>>> import os
>>> os.listdir()
[‘boot.py’, ‘bme280.py’, ‘max44009.py’]
测试传感器数据
>>> import machine
>>> import bme280
>>> i2c = machine.I2C(scl=machine.Pin(5), sda=machine.Pin(4))
>>> bme = bme280.BME280(i2c=i2c)
>>> print(bme.values)
(‘20.73C’, ‘1020.55hPa’, ‘24.31%’)
>>> import max44009
>>> lum = max44009.MAX44009()
>>> print(lum.luminosity())
3.06
一切正常。
在raspberry pi上做个简单http接口收集数据,代码如下:
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import time
def getNowTime():
return time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %T',time.localtime(time.time()))
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#try:
lum = self.get_argument("lum")
hum = self.get_argument("hum")
temp = self.get_argument("temp")
press = self.get_argument("press")
f = open("./gy39.log", "a")
tmpData = "%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (getNowTime(), lum, hum, temp, press)
f.write(tmpData)
f.close()
#except:
# pass
self.write("ok")
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/", MainHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(9999)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
ESP8266的调用传感器代码
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Revision:
# Author: simonzhang
# Email: simon-zzm@163.com
# Web: www.simonzhang.net
# -------------------------------
# http://192.168.3.212:9999/?lum=12&hum=3.43&temp=23423&press=12132
class timegy30():
def run():
import machine
#
import bme280
i2c = machine.I2C(scl=machine.Pin(5), sda=machine.Pin(4))
bme = bme280.BME280(i2c=i2c)
temp = bme.values[0][:-1]
press = bme.values[1][:-3]
hum = bme.values[2][:-1]
#
import max44009
lum = max44009.MAX44009()
lum = lum.luminosity()
url = "http://192.168.3.212:9999/?lum=%s&hum=%s&temp=%s&press=%s" % \
(lum, hum, temp, press)
#
import urequests
urequests.get(url)
ESP8266启动调用定时器,代码main.py。
from machine import Timer
tim = Timer(1)
def func(t):
import timetask
timetask.timegy30.run()
tim.init(period=3000, mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=func)
raspberry日志上看跑了8个多小时,收集9千多次,应该是没有丢的情况,因为中间断了一小会。
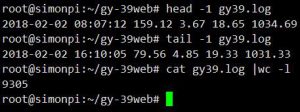
电量使用43mha,每小时是5.3MHA。
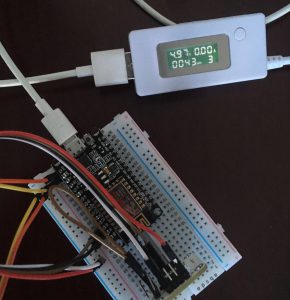
充电宝3.7v 1800MHA电芯是10块左右。接在这板子上按照3秒测试、发送一次的速度是不能用15天。如果是5分钟发一次,是不是能用150天,电池这部分我不确定,我这个也没有稳压板。我这测试好像比网上测试的耗电量都低。
后续如果优化应该有3部分。
1)cpu频率按照计算量降到最低。
2)关闭没有用的端口。
3)优化代码,设计睡眠模式。
ESP8266的看门狗和自动重启结合使用防止宕机。
使用功能mqtt进行收发,此芯片用在物联网上相当不错。
raspberry python3 gy-39
买了一片GY-39,不小心短路了,mcu好像就烧坏了。不过传感器还是好的,就直接用传感器。

上面有两个传感器bme280测试温度、湿度、气压。max44009测试光照。
用i2c接口将数据线连接好,到raspberry pi上查看设备。
root@simonpi:~# i2cdetect -y 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: — — — — — — — — — — — — —
10: — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
20: — — — 23 — — — — — — — — — — — —
30: — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
40: — — — — — — — — — — 4a — — — — —
50: — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
60: — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
70: — — — — — — 76 —
通过文档查看max4400用到的地址是1001 010x或1001 011x。
所以地址4a是MAX44009,地址76就是BME280。
可直接用pip3安装bme280的包,我为了方便直接提取了。
执行附件中的测试脚本测试通过
raspberry-esp280-max44009源码
raspberry python3 PWM MG90S
因为python2马上就要不维护了,以后就用python3了。
apt-get install python3-pip
pip3 install RPi.GPIO
棕色线接地
红色线接5V
黄色线是信号线
信号线接在gpio23上,输入相应的角度后舵机会转动到相应角度。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Revision:
# Author: simonzhang
# Email: simon-zzm@163.com
# Web: www.simonzhang.net
# -------------------------------
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
SERVO = 23
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(SERVO, GPIO.OUT)
p = GPIO.PWM(SERVO, 2)
p.start(0)
try:
while True:
desc = input("0-100:")
dc = float(desc)
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
p.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
p.stop()
GPIO.claeanup()